In this article we will be looking at the health benefits of Intermittent Fasting, which is an eating pattern that alternates between fasting and time-restricted eating periods.
There are several different types of intermittent fasting patterns:
The 16:8 intermittent fasting plan involves 16 hours of fasting followed by an eight-hour eating period.
The alternate-day fasting plan is characterized by fasting every other day, where you consume no calories or drastically reduce your calories consumed to around 500 to 600 calories.
The 5:2 fasting approach involves eating normally for five days a week and restricting calorie intake to around 500 to 600 calories on two non-consecutive days.

Cellular Changes That Prove the Health Benefits of Intermittent Fasting
Intermittent fasting triggers a cascade of cellular events that contribute to its potential health benefits.
Here’s a breakdown of the health benefits of intermittent fasting at the cellular level:
Metabolic Shifts
- Glucose Utilization: As blood sugar levels drop, the body switches from primarily using glucose for energy to utilizing stored glycogen.
- Fat Breakdown: Once glycogen stores are depleted, the body begins breaking down fat for energy, a process known as lipolysis.
- Ketone Production: In prolonged fasting, the liver converts fatty acids into ketones, an alternative energy source for the brain and other tissues.
Cellular Repair and Renewal
- Autophagy: This process is significantly enhanced during fasting. It involves the breakdown and recycling of damaged cellular components, promoting cellular renewal and potentially reducing the risk of neurodegenerative diseases.
- Mitophagy: A specific type of autophagy targeting damaged mitochondria, the cell’s powerhouses. This process helps maintain cellular energy production.
Hormonal Changes
- Insulin Sensitivity: Fasting can improve insulin sensitivity, allowing cells to respond better to insulin and utilize glucose more effectively.
- Growth Hormone: Levels of human growth hormone (HGH) may increase, which can contribute to muscle growth, fat loss, and improved sleep.
Gene Expression
- Adaptive Responses: Fasting can influence the expression of genes involved in metabolism, stress response, and longevity.
- Cellular Protection: Some genes related to cellular protection and repair may be upregulated during fasting.
Here are the top 5 health benefits of intermittent fasting:
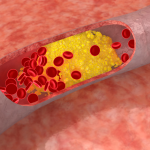
- Weight Loss and Fat Reduction:
- Intermittent fasting (IF) can be an effective strategy for weight loss.
- By cycling between periods of eating and fasting, IF helps reduce overall calorie intake.
- Lower insulin levels, increased human growth hormone (HGH), and elevated norepinephrine levels promote fat breakdown and improve metabolism.
- Studies show that participants following various IF methods lost 0.8–13% of their baseline body weight.
- 2. Heart Health Improvement:
- IF may lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure, contributing to better heart health.
- By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, IF supports cardiovascular well-being.
- Regular fasting may protect against heart disease and related risk factors.
- 3. Cellular Repair and Longevity:
- During fasting, important cellular repair processes occur, including waste removal from cells.
- Changes in gene expression related to longevity and disease protection are observed.
- IF promotes overall cellular health and may contribute to a longer, healthier life.
- 4. Enhanced Brain Function:
- IF may improve brain health by enhancing brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) levels.
- BDNF supports cognitive function, memory, and mood regulation.
- Fasting also stimulates autophagy, a process that removes damaged cells and supports brain health.
- 5. Regulation of Circadian Rhythm and Sleep:
- IF helps regulate the body’s internal clock (circadian rhythm).
- By aligning eating patterns with daylight hours, IF improves sleep quality.
- Proper sleep is essential for overall health and well-being.
In summary, there are several health benefits of intermittent fasting, including weight management, heart health, cellular repair, brain function, and improved sleep. As with any dietary change, it’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting an intermittent fasting regimen.
Important to note: Intermittent fasting is not a diet. It’s a pattern of eating. What you eat during your eating window is still crucial for overall health.
Would you like to know more about the potential health benefits of intermittent fasting or how to start? Click here to find out more
Pharm Chee Recommends:
Dr Berg’s Guide to Intermittent Fasting
You can watch this video to get you started on the right track to unlock the health benefits of intermittent fasting
To purchase a wide range of natural health and wellness products from our website, click here
![]()